Electricity has existed since the beginning of the universe, as it originates from atoms and their charged particles. However, humans began harnessing this powerful form of energy only about 200 years ago. Today, whether generated from natural or artificial sources, the production and use of electricity can be categorized into distinct types.
Broad classification of electricity

Static Electricity: As the name suggests, static electricity refers to stationary electric charges. It occurs due to an electrical imbalance within atoms. Common examples of static electricity include lightning, sparks when touching a metal object, and a plastic comb attracting small paper pieces.
Current Electricity: In current electricity, electric charges are in motion. The term “current” signifies movement, similar to a “water current” that refers to the flow of water. Likewise, the flow of positive charges through a conductor over a specific period is what we define as electric current. This is the type of electricity that passes through wires and runs our electrical appliances, such as bulbs, fans, motors, TV, radio, mobile phone, computers, etc.
There are two types:
* Direct Current (DC)
* Alternating Current (AC)
Direct Current (DC): In direct current, electrical parameters like voltage and current are fixed. They do not vary with time. It means that the direction of current in a conductor is always the same.
In the figure, the red line is a graph of DC voltage that is fixed at 24 V.
- Sources of DC are batteries, solar cells, DC generators, AC to DC converters (rectifiers)
- All electronic devices run only on direct current

Alternating Current (AC): Unlike direct current (DC), where both voltage and current remain constant, alternating current varies with time in a cyclical pattern. During the first half of the cycle (0° to 180°), the voltage is positive, and current flows in one direction. In the second half of the cycle (180° to 360°), the voltage becomes negative, causing the current to flow in the opposite direction.
There are two types of AC:
* Single phase
* Three phase
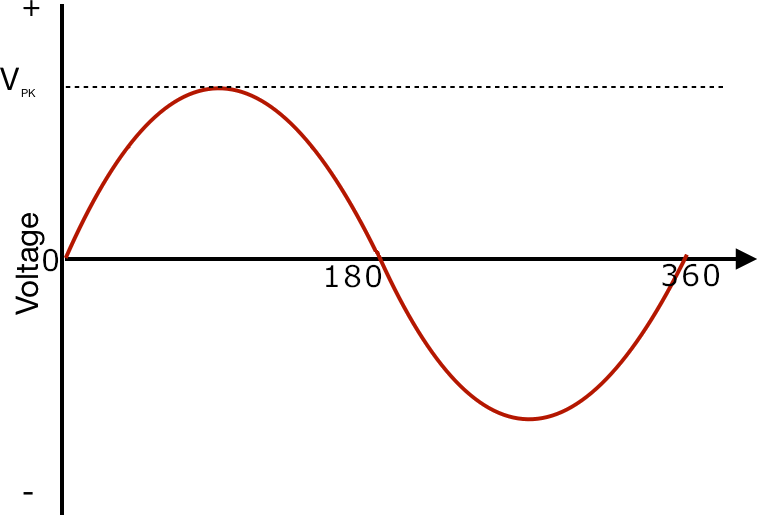
Single phase AC: In a single-phase AC system, there is one wave, as shown in the diagram above. The electric circuit consists of two wires: one is called the live (or line) wire, and the other is the neutral wire. Single-phase voltage and current are commonly used to power small electrical loads such as light bulbs, fans, and household appliances.
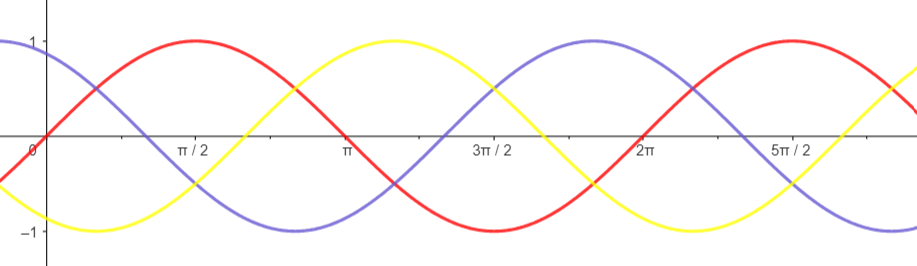
Three phase AC: A three-phase AC system consists of three separate phases, with each wave offset by 120° from the others. It uses three wires, typically labeled Red, Yellow, and Blue, to carry current, along with a neutral wire for return. This type of system is commonly used to supply power to large electrical loads, such as heavy-duty motors, industrial equipment, and commercial machinery.


Pingback: JJ
Pingback: Kim